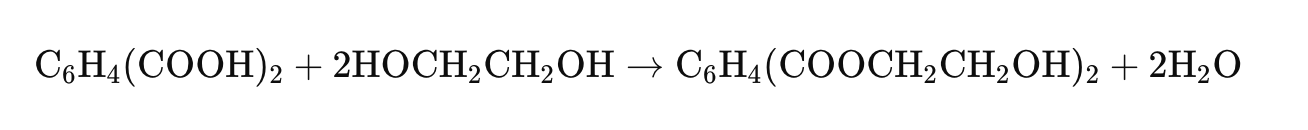The Journey of Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET): From Raw Material to Everyday Essential
PET Polyethylene Terephthalate is now everywhere. From water bottles and food containers to synthetic fibers and packaging materials, PET has become an indispensable part of our daily lives. According to a 2023 report by Grand View Research, the global PET market size was valued at USD 27.3 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.8% from 2023 to 2030. This surge is driven by the increasing demand for sustainable and recyclable materials. But how is this versatile polymer made? Let's delve into the fascinating process of creating PET.
What is PET?
Polyethylene Terephthalate, commonly known as PET, is a type of polyester made by the polymerization of ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid. This material is renowned for its strength, transparency, and recyclability, making it a popular choice for a wide range of applications, particularly in packaging and textiles.
The Raw Materials: Ethylene Glycol and Terephthalic Acid
The production of PET starts with two primary raw materials: ethylene glycol (EG) and terephthalic acid (TPA). Ethylene glycol is a colorless, odorless liquid derived from ethylene, a byproduct of petroleum refining. Terephthalic acid, on the other hand, is a white crystalline powder typically produced from paraxylene, another petroleum derivative.
The Polymerization Process
The manufacturing of PET involves a series of chemical reactions that transform ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid into long chains of PET polymer. This process can be broken down into several key steps:
1. Esterification
The first step in PET production is esterification. In this stage, ethylene glycol reacts with terephthalic acid under heat and pressure to form bis(2-hydroxyethyl) terephthalate (BHET) and water. This reaction is facilitated by catalysts such as antimony, germanium, or titanium compounds. The esterification reaction can be represented as follows:
2. Pre-Polymerization
Following esterification, the BHET undergoes pre-polymerization, where the molecules start linking together to form short chains. This step occurs under vacuum to remove the water and any unreacted monomers, resulting in a pre-polymer with moderate molecular weight.
3. Polycondensation
The final and most crucial step is polycondensation. In this stage, the pre-polymer is further heated under reduced pressure to drive off any remaining water and increase the molecular weight of the polymer chains. The polycondensation reaction produces high-molecular-weight PET, which has the desired properties of strength, clarity, and durability.
Forming PET Products
Once the PET polymer is synthesized, it can be processed into various forms depending on its intended use. Here are some common methods:
1. Injection Molding
Injection molding is a widely used technique for creating PET bottles and containers. The PET resin is heated until it melts and then injected into a mold. After cooling, the mold is opened, and the finished product is ejected.
2. Extrusion
Extrusion is another common method used to produce PET films and sheets. The melted PET is forced through a die to create a continuous shape, which is then cooled and cut into desired sizes.
3. Blow Molding
Blow molding is particularly used for making hollow objects like bottles. In this process, a preform (a small test-tube-shaped piece of PET) is heated and then expanded by blowing air into it, forming the final shape of the container.
Recycling PET
One of the significant advantages of PET is its recyclability. Post-consumer PET products can be collected, cleaned, and melted down to create new PET items, reducing the environmental impact. In 2022, the recycling rate for PET bottles in the United States was approximately 29.1%, highlighting the growing awareness and efforts towards sustainable practices.
Wankai: Leading the Way in PET Production
For industries looking to source high-quality PET, Wankai is a leading producer of both bottle-grade and non bottle-grade PET chips. With applications ranging from packaging and textiles to automotive and construction, Wankai's PET products meet diverse industry needs while ensuring top-notch quality and sustainability.
The journey of Polyethylene Terephthalate from raw materials to the final product is a remarkable blend of chemistry and engineering. Its widespread use and recyclability make PET a pivotal material in our modern world. Whether in the form of a water bottle, a food container, or a piece of clothing, PET's impact is profound and far-reaching. As the demand for sustainable materials continues to grow, innovations in PET production and recycling will undoubtedly play a crucial role in shaping a greener future.